DataBank and Georgia Tech pioneer sustainable HPC Data Center in Tech Square
Project at a Glance | |
|---|---|
| Location | Midtown Atlanta, Georgia, USA |
| End User | Georgia Institute of Technology |
| Integrator / Partner | DataBank |
| Application | High-Performance Computing (HPC) |
| Legrand Solution | ColdLogik Rear Door Coolers from USystems |
| Key Results | Less energy used for cooling from heat reuse |
Creating a Future-Ready HPC Ecosystem
The DataBank ATL1 data center is not your average data center.
When Georgia Tech set out to create a high-performance computing center for their institution, they turned to DataBank to build a data center environment capable of meeting the performance needs of the center, and overcoming the inherent challenges that often accompany HPC initiatives.
DataBank’s ATL1 facility will be located in the new CODA building of Georgia Tech’s Technology Square, smack dab in the middle of the Atlanta’s tech hub, where academia meets innovation, research, and fortune enterprises. ATL1 will not only be different from any other DataBank facility, it will be will be one of the most advanced data centers in the country.
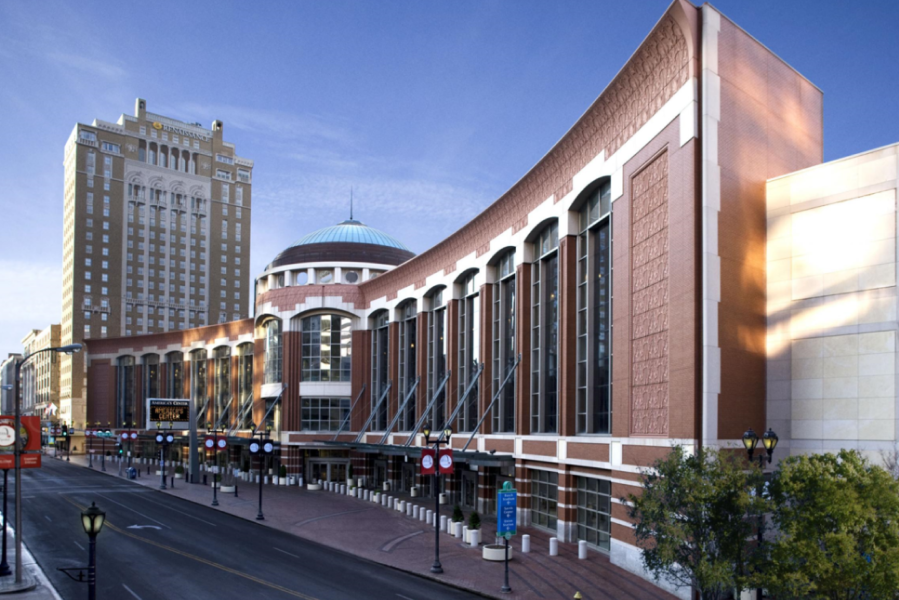

Midtown Atlanta Data Center The Midtown Atlanta Data Center is part of the CODA development,
a 645,000 sqft mixed-use office complex, currently under construction in Georgia Tech’s Technology Square.
Right out of the gate, ATL1 will possess two things unique to any data center in the region:
Southern Crossroads (SoX) & The Georgia Tech Supercomputer
The Challenge
DataBank offers a full range of connectivity methods across the nation to achieve our customers goals. This includes a national IP transport service which provides inter-region and intra-metro connectivity. Our carrier neutral facilities offer robust interconnectivity and high-bandwidth access to top-tier carriers. This results in a resilient communication environment across multiple DataBank sites.
That system alone would represent a major innovation in data center cooling But, in our mission to continuously evolve the data center experience, DataBank took the implementation one step further.
In recap, the project demanded:
High-density computing capabilities
Low-latency network infrastructure
Advanced sustainability and heat reuse strategies
The Solution
In the typical data center environment, any heat removed with CRAC units is usually sent back to the central plant, exchanged for condenser water, and receded off the roof via typical heat rejection. Instead of wasting the heat, the ATL1 facility is actually sending it over to the CODA building’s high-rise boilers and allowing tenants to reuse and repurpose it to heat their offices in colder weather, thus further offsetting energy use.
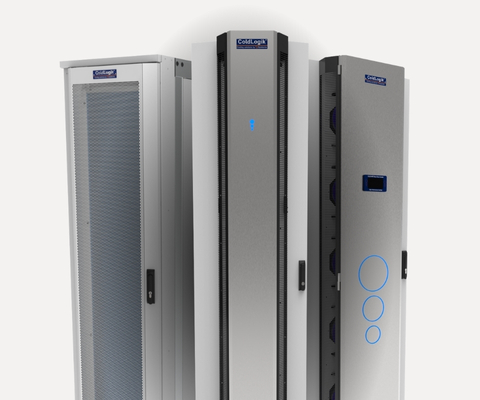

Discover Our Rear Door Heat Exchangers (RDHx)
A Rear Door Heat Exchanger (RDHx) is an energy-efficient cooling solution installed directly on the back of a server rack. It captures and removes heat at the source using chilled water, significantly reducing the demand on traditional room cooling.

By using ColdLogik's Rear Door Heat Exchangers, DataBank and Georgia Tech are cooling 50 kW per enclosure, per rack, using 73-degree warm water. And this rear door cooling system can use that same capacity to cool up to 100 kW per rack with just minor changes in infrastructure.
The Result
The ATL1 data center is more than just a facility — it's a living lab for sustainable digital infrastructure and a beacon for the next generation of green innovation.
50–100 kW per rack cooling using warm water
Up to 80% real estate savings vs. traditional cooling
90% less energy used for cooling
Reused thermal energy to heat office space in winter months
Fully integrated with Southern Crossroads (SoX) for research network connectivity
Being able to cool 50 kW with 73 degree, and able to go 100 kW in the same footprint? That’s unheard of.
Discover some of our other cases
_____

Data Center Insights: Edition 5




















 Canada
Canada
 Latin America (English)
Latin America (English)
 Latin America (Espanol)
Latin America (Espanol)
 USA
USA
 China
China
 India
India
 Japan
Japan
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 South East Asia (English)
South East Asia (English)
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 France
France
 Germany
Germany
 Italy
Italy
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Spain
Spain
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Turkey
Turkey
 UK
UK
 Africa (english)
Africa (english)
 Africa (français)
Africa (français)
 Middle East (english)
Middle East (english)
 Australia
Australia
 New Zealand
New Zealand
