Understanding Rack ‘U’-Space for Efficient Data Center Design
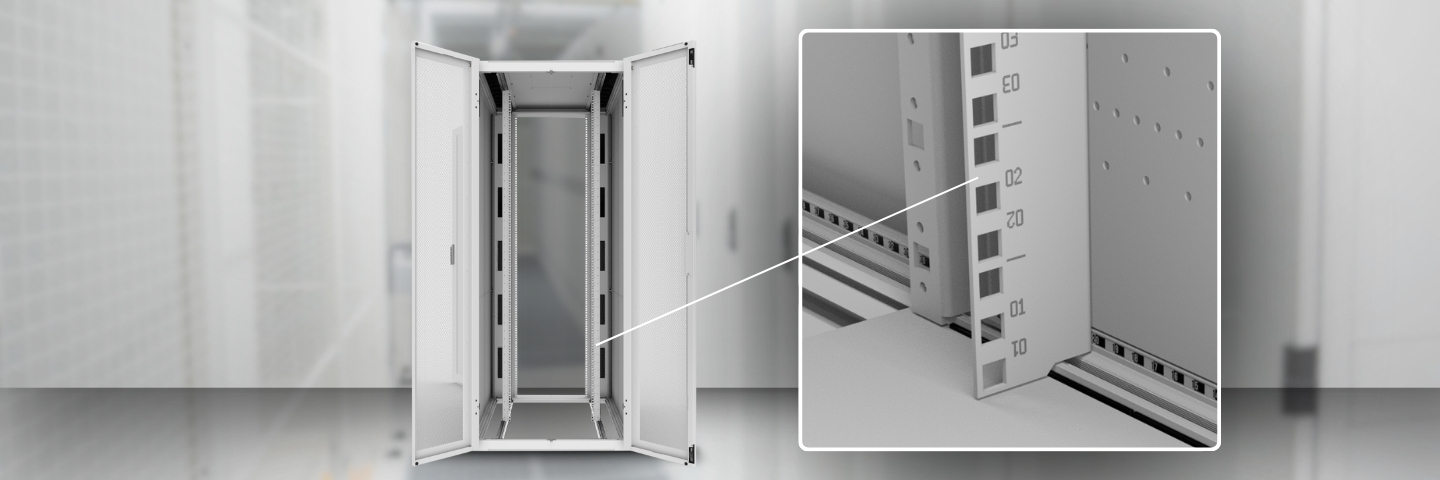

In today’s high-density data centers, where every inch of space matters, understanding how to define and manage rack unit (U) space is a critical part of planning for power, cooling, cable management, and future scalability.
In this blog, we explore what U-space means, why it matters, and the key considerations when selecting the right cabinets and rack PDUs to optimize space for maximum performance, flexibility, and adaptability.
What is U-Space, and Why It Matters
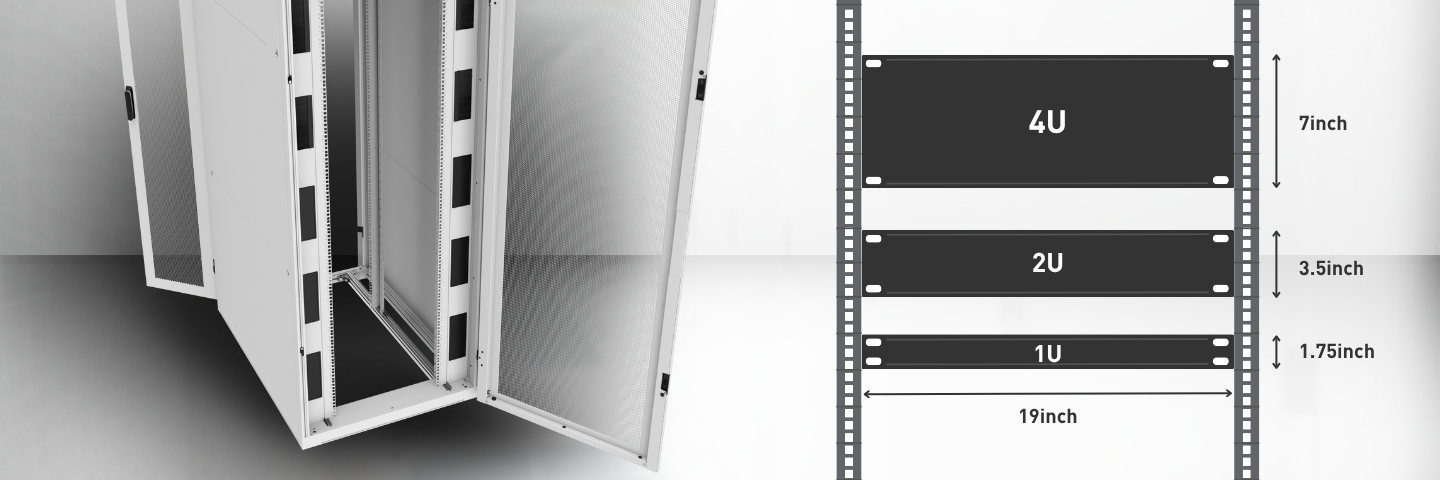
A “U” or “RU” stands for a rack unit and is the standard measurement used to define the mountable height within a server rack, with one U equal to 1.75 inches (44.45 mm). This standard, introduced by the Electronic Industries Association (EIA), ensures compatibility between racks and equipment from different manufacturers.
Each rack follows standardized vertical mounting patterns, consisting of three square or circular holes measuring 1U (1.75 inches). Most servers occupy 1U, 2U, or 4U of space, while larger hardware can take up to 9U and 12U.
Typical racks are commonly built around standardized heights, such as 42U, 47U, 48U, or even 52U in higher-density environments. To calculate the number of rack units a device occupies, divide its height by 1.75 inches. For example, for a 3.5-inch device, the calculation would be 3.5 / 1.75 = 2U.

Understanding U-space is essential for several reasons:
- Space optimization: Understanding how much usable space each device consumes helps you maximize rack density.
- Futureproofing: Available U-space ensures smooth upgrades as IT equipment evolves.
- Cooling and airflow: Rack height and configuration directly influence airflow patterns, containment design, and cooling efficiency.
- Power distribution: The choice of power distribution units (PDUs) affects available U-space and how easily power can be managed within the rack.
Why Rack U-Space Optimization Matters for Power and Cooling Efficiency
Key Considerations for Cabinets, PDUs, and Layout:
Cabinets: Depth, Width and Accessibility

While rack height is defined by U-space, depth and width vary by manufacturer and application. Selecting the correct cabinet dimensions has a significant impact on both accessibility and airflow.
- Depth: Standard racks are 800, 1000, or 1200 mm (31.5, 39.4 or 47.2 inches) deep, but deeper cabinets may be necessary for modern, high-density servers or additional cooling components.
- Height (U count): While 42U racks were once the standard, 47U and 48U cabinets are now the most common in modern data centers. Taller 52U racks are also becoming more popular for facilities targeting higher compute density.
- Width: The industry standard is 19 inches of internal rail spacing for a full rack.
- Cable and cooling access: Cabinets that integrate efficient cable channels and airflow management features support easier maintenance and better cooling performance.
PDU Placement: Horizontal vs Vertical
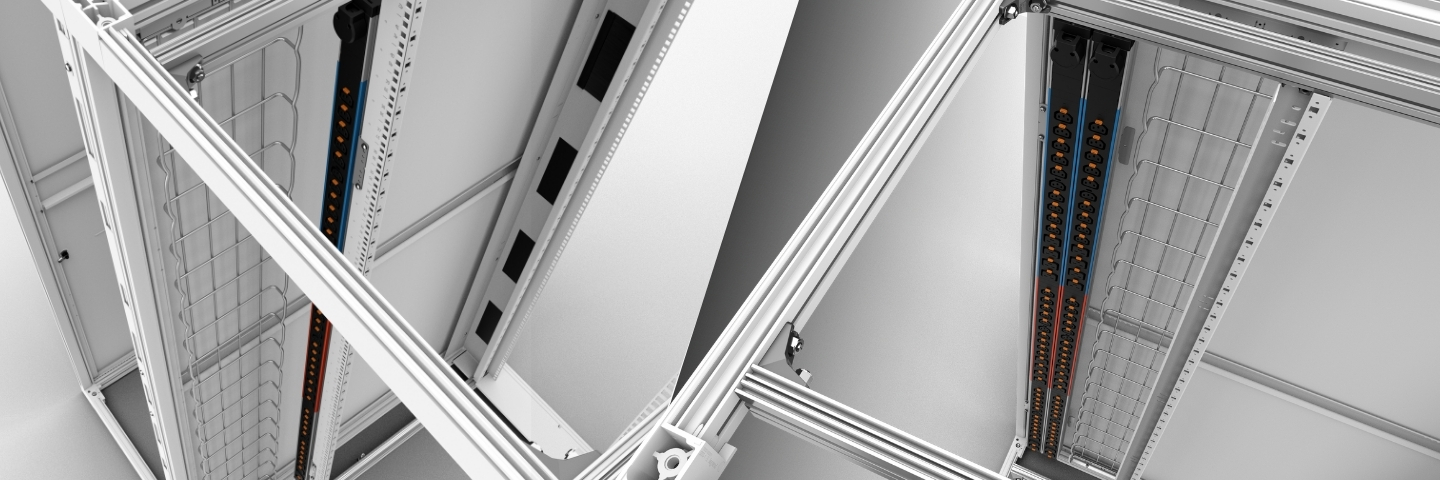

One of the most impactful decisions in U-space planning involves how PDUs are mounted within the rack.
- Horizontal PDUs (also known as ‘rackmount PDUs’) are mounted like servers and typically occupy 1U or 2U of valuable rack space.
- Vertical PDUs (also known as ‘rack PDUs’) are mounted along the side or rear of the cabinet, taking up Zero U rack space and thereby freeing up additional space for IT equipment.
- Choosing vertical (Zero U) PDUs allows more space for servers and networking gear and simplifies airflow management by avoiding obstructions. It also improves accessibility, as maintenance can often be done without disturbing the main server stack. In addition, cable management is also easier because the outlets in the PDU are closer to each server.
Planning for Dense Equipment and Mixed Generations
Modern data centers are rarely uniform. Racks may contain 1U, 2U, 4U, or even 12U devices, as well as dense networking and storage appliances. This mix creates varying demands for power, cooling, and physical space.
To manage this effectively:
- Map your current and planned U-space per rack.
- Allow for future upgrades or larger equipment.
- Avoid top-heavy configurations that restrict airflow or create imbalance.
- Plan entry points for cables and power carefully to prevent wasted U-space.
How Legrand Data Center Solutions Support Smarter U-Space Planning
Legrand’s range of data-center solutions, which include racks and cabinets, intelligent rack PDUs, and cable management systems, are engineered to help you maximize U-space, manage density, and ensure long-term scalability.
- Cabinet flexibility: Legrand’s modular cabinets offer adjustable rails, multiple depth options, and integrated airflow management for a precise fit to your environment.
- Zero-U PDUs: Our vertical PDUs preserve every rack unit for mission-critical IT equipment while offering intelligent power monitoring and management.
- Integrated design: Combining power, cooling, and cable management within the same modular framework reduces clutter, improves efficiency, and futureproofs your setup.
- Consultative approach: Legrand can work with you to customize cabinets and PDUs to fit your specific needs.
By aligning U-space planning with cabinet selection, PDU strategy, and airflow design, you create an infrastructure that is efficient today and ready for tomorrow’s workloads.
Looking Ahead: U-Space in an AI-Driven Data Center
With data centers facing unprecedented power and density requirements, racks now need to accommodate heavier servers, GPU clusters, liquid-cooling units, and high-capacity PDUs. Understanding U-space measurements is therefore critical when selecting cabinet systems and rack PDUs to avoid compromising space, cooling, or scalability.
Legrand can help you make the most of every U. With the right combination of modular design, intelligent power distribution, and scalable infrastructure, your data center can remain efficient, adaptable, and ready for whatever comes next.
To learn more about Legrand’s cabinets, visit here. To explore more about our rack PDU solutions, see here.



















 Canada
Canada
 Latin America (English)
Latin America (English)
 Latin America (Espanol)
Latin America (Espanol)
 USA
USA
 China
China
 India
India
 Japan
Japan
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 South East Asia (English)
South East Asia (English)
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 France
France
 Germany
Germany
 Italy
Italy
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Spain
Spain
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Turkey
Turkey
 UK
UK
 Africa (english)
Africa (english)
 Africa (français)
Africa (français)
 Middle East (english)
Middle East (english)
 Australia
Australia
 New Zealand
New Zealand