The Impact of AI on Data Centers: Challenges and Solutions
Discover how AI is transforming data centers and explore Legrand's innovative solutions for power, cooling, and security challenges.
Introduction
The growth of AI applications has revolutionized the data center industry, bringing significant challenges. One of the foremost concerns is the increased power consumption and high-power density environments that AI demands, significantly impacting the physical infrastructure requirements of data facilities.
Historical Context of Data Center Power Density
In the late 1970s, data center power density was generally between 2 kW and 4 kW. Today, it is not uncommon to exceed 40 kW to accommodate AI or HPC (high-performance computing) workloads. In November, Silicon Valley Power revealed that its forecasted annual data center load in 2035 "almost doubles the current system load."
Changes in Data Center Infrastructure
Traditional Infrastructure
Colm Shorten, Senior Director of Data Centers at JLL Real Estate, highlighted the consistency of data center infrastructure over the past two decades:
"It's true to say that data center infrastructure hasn't changed a great deal in 20 years, so there are models of design that are used repeatedly, whether they're based on uptime or five-nine availability."
Traditional designs focused on ensuring the data center runs, has power, network, cooling, and security, typically running between 8 to 12 kW, with 19 kW considered high.
Impact of AI on data center demands
AI has disrupted traditional power requirements, increasing rack density and power requirements. As Shorten explains:
"What AI has done in a disruptive sense is that it's challenged what those power requirements are, so rack density and rack power requirements have increased. If you generate a lot of power, you generate a lot of heat. If you generate a lot of heat, you’ve got to dissipate that heat and get rid of it."
David Bradley, Regional Director of Ireland and Central Eastern Europe at Legrand Data Center Solutions, emphasized the need for new cooling strategies:
"There needs to be a mind shift now on how we cool these racks and how we deliver the power racks based on the demands from AI."
Challenges AI Places on the Data Center Industry
Increasing Power Density
As computing power and chip designs advance, equipment racks double in power density every six to seven years. The Uptime Institute reports that over a third of data center operators say their densities have "rapidly increased" in the past three years. AI server cluster densification necessitates a shift from air to liquid cooling, introducing challenges such as site constraints, obsolescence risks, installation complications, and limited sustainable fluid options.
Complexity of AI Workloads
AI workloads add another layer of complexity, requiring cost-efficient training that is less latency-dependent. Shorten explains the shift in data center placement:
"In the past, we would typically find a site that's within either a cloud region or a densely populated metro, build a data center there, and bring the power to it. Now you bring the data center to the power."
Bradley adds:
"Training AI is not latency-dependent, so it might mean that you could actually deploy new data centers somewhat outside of the central FLAPD region."
Network and Redundancy Requirements
The surge in AI demands intensifies network requirements, placing added stress on data centers to ensure robust connectivity and low latency. High-reliability mechanisms and seamless switching between power sources are necessary to prevent downtime. Power surges and harmonic distortions caused by non-linear components pose continual threats to efficiency and safety, often leading to overheating issues.
Future-Proofing Facilities
Shorten emphasizes the need for hybrid solutions to avoid obsolescence:
"We have to develop what's called a hybrid solution because if we build a pure traditional model, there’s a risk of it becoming obsolete in two to four years' time."
Physical Infrastructure Challenges
AI's demands on physical infrastructure are significant. For example, the weight and cooling requirements of AI equipment can exceed the design limits of older data centers. Bradley notes:
"You could add 200 to 300 kg of weight on a rack. Now, what you've got is a floor that cannot take that."
Regulatory and Sustainability Challenges
Regulatory frameworks struggle to keep pace with technology, complicating compliance for data center operators. Sustainability goals also become harder to meet as AI increases energy consumption. According to the 2022 Data Center Industry Survey by the Uptime Institute, 63 percent of data center operators expect mandatory sustainability reporting in the next five years. The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) will impact some EU-based businesses from January 1, 2024, necessitating new metrics like water and carbon use effectiveness.
Security Risks
AI introduces new security risks, including automated attacks and vulnerability identification. Nearly 40 percent of organizations have experienced major outages due to human error since 2020. Advanced encryption, biometric authentication, and cybersecurity solutions are essential to counter unauthorized access and monitor for anomalies.
Shorten highlights the dual nature of AI in security:
"From a security standpoint, AI is kind of a double-edged sword. The positive is that AI is very good if you were to apply it to look at changes in patterns. The flip side is that it's very powerful and can be used by bad actors."
Solutions to AI-Induced Challenges
How to Manage Thermal Issues in Data Centers?
Legrand offers innovative designs like USystems’ Rear Door Coolers, which optimize thermal management by removing heat at the source and preventing hot exhaust air from entering the data room. These coolers allow load removal of up to 92 kW per cabinet.
Advanced Cooling Methods
Legrand's liquid cooling solutions, such as direct-to-chip or immersion cooling, are increasingly adopted to manage high-density environments, dissipating heat more effectively than traditional air-cooling methods.
Intelligent Power Distribution
Legrand provides intelligent rack power distribution units (PDUs) like the Raritan PX4 and the Server Technology PRO4X, designed to handle the high power consumption and density AI brings. These PDUs offer high-density outlet technology and intelligence features catering to complex AI requirements.
Customization
Legrand's customizable cabinets and modular solutions provide the flexibility and scalability required to accommodate future growth. Track Busway solutions with monitoring points can identify potential energy efficiency and reliability improvements.
Enhancing Physical Security
Legrand's intelligent cabinet locking systems, such as Nexpand’s Smart Lock, meet regulatory compliance mandates and work with video surveillance solutions. Our intelligent PDUs are equipped with the latest network security protocols, diverse authentication options, and best-in-class data encryption methods.
Promoting Energy Efficiency
Adopting energy-efficient hardware and renewable energy sources is crucial to reduce operating costs and carbon footprint. Legrand's environmental monitoring devices like Raritan's SmartSensors enable precise cooling management, minimizing energy waste and predicting potential equipment failures.
Get Your Data Center AI-Ready
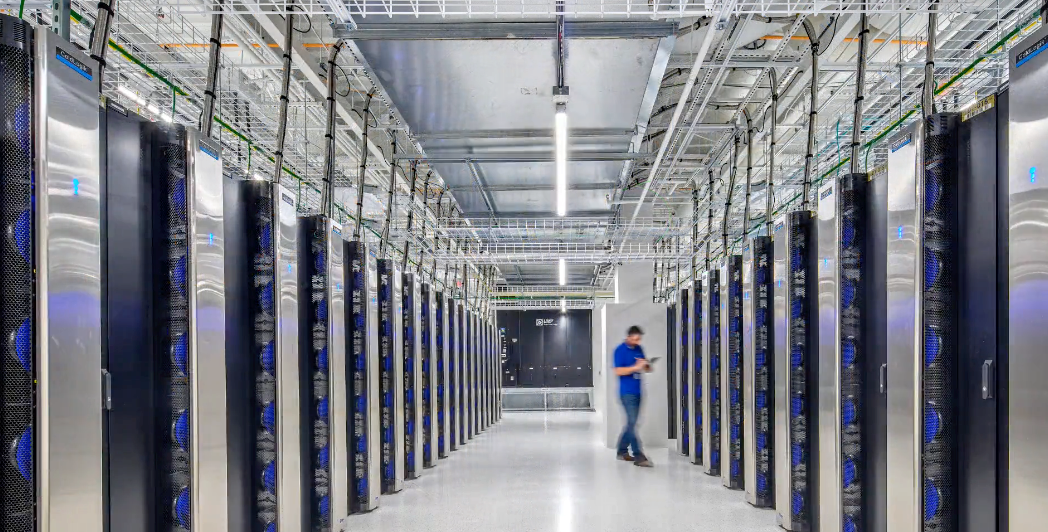

Discover how Legrand’s innovative solutions can meet the power and cooling demands of AI in your data centers.



















 Canada
Canada
 Latin America (English)
Latin America (English)
 Latin America (Espanol)
Latin America (Espanol)
 USA
USA
 China
China
 India
India
 Japan
Japan
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 South East Asia (English)
South East Asia (English)
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 France
France
 Germany
Germany
 Italy
Italy
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Spain
Spain
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Turkey
Turkey
 UK
UK
 Africa (english)
Africa (english)
 Africa (français)
Africa (français)
 Middle East (english)
Middle East (english)
 Australia
Australia
 New Zealand
New Zealand