Row Based Cooling: Precision Data Center Cooling Next to the Load
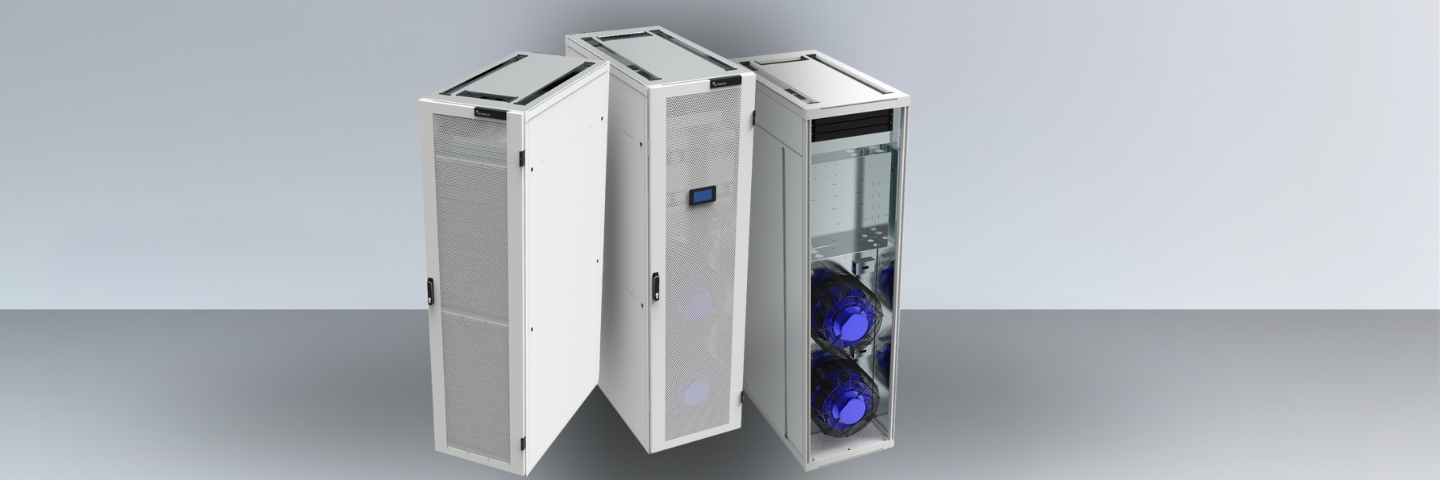

Row based cooling delivers targeted thermal management by placing cooling units directly between server racks, offering superior efficiency and control compared to traditional perimeter cooling systems. This close-coupled approach supports power densities of 10–30+ kW per rack while providing modular scalability for modern data center demands.
What Is Row Based Cooling?
Row based cooling, also called in-row cooling or close-coupled cooling, positions cooling units directly within server rack rows rather than around the data center perimeter. This strategic placement creates shorter airflow paths and more precise temperature control by bringing the cooling source as close as possible to the heat generation point.
How Row Based Cooling Works
Air circulation process:
- Hot air intake – Units draw heated air from server rack rear panels
- Cooling process – Air passes through chilled water or refrigerant coils
- Cold air delivery – Cooled air returns to rack front intakes
- Continuous circulation – Process repeats for consistent temperature control
Key components:
- Cooling coils (chilled water or DX refrigerant)
- Variable speed fans for airflow control
- Temperature and humidity sensors
- Control systems for automated operation
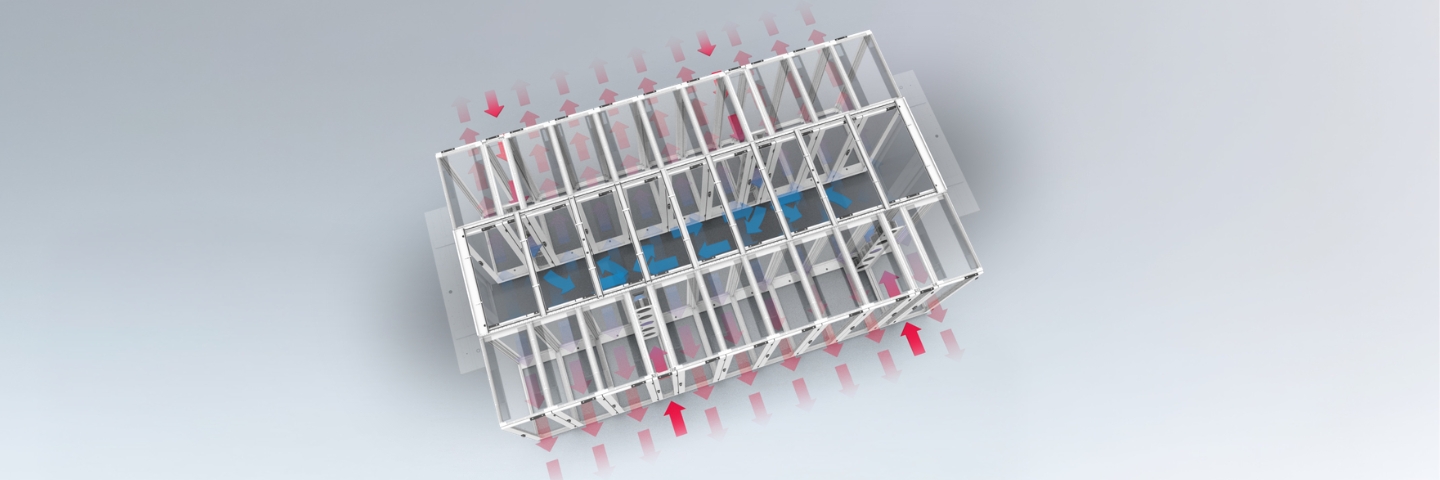
Why Choose Row Based Cooling?
Modern data centers face increasing thermal challenges from high-density computing, AI workloads, and unpredictable heat patterns. Row based cooling addresses these challenges through proximity-based thermal management, offering superior control and efficiency compared to traditional perimeter cooling systems that struggle with hot spots and inefficient airflow patterns.
Primary Applications
| Environment Type | Power Density Range | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Enterprise Data Centers | 10–25 kW per rack | Precise control, energy efficiency |
| Edge Computing | 5–20 kW per rack | Compact footprint, modular deployment |
Key Benefits of Row Based Cooling
Row based cooling delivers measurable improvements in energy efficiency, operational control, and thermal management compared to traditional cooling approaches. By positioning cooling units directly adjacent to heat sources, these systems eliminate many of the inefficiencies that plague perimeter-based cooling architectures.
1. Cooling Efficiency
- Minimal air mixing – Direct hot-to-cold air path reduces bypass airflow
- Reduced energy waste – Shorter airflow distances improve system efficiency
- Precise temperature control – Cooling delivered exactly where needed
2. Enhanced Scalability
- Modular deployment – Add cooling capacity as IT loads increase
- Independent operation – Each unit operates autonomously
- Flexible configuration – Supports various rack densities within same row
3. Improved Control and Monitoring
- Zone-level management – Individual unit monitoring and control
- Real-time adjustments – Responsive to changing heat loads
- Integration capability – Works with building management systems
Technical Configurations
Row based cooling systems are available in several technical configurations, each optimized for different deployment scenarios and infrastructure requirements. The choice between chilled water and direct expansion systems, along with containment strategies, significantly impacts performance, efficiency, and installation complexity.
Chilled Water-Based Systems
Best for: High-density applications requiring maximum efficiency
Features:
- Connection to central chilled water loop
- Superior heat removal capacity
- Energy-efficient operation
- Scalable for large deployments
DX (Direct Expansion) Systems
Best for: Smaller deployments or remote locations
Features:
- Self-contained refrigeration system
- No chilled water infrastructure required
- Quick installation and commissioning
- Ideal for edge computing environments
Containment Integration
Cold Aisle Containment:
- Encloses cold air supply
- Prevents hot air infiltration
- Maximizes cooling efficiency
Hot Aisle Containment:
- Captures server exhaust heat
- Directs hot air to cooling units
- Reduces cooling system workload
Implementation Considerations
Successful row based cooling deployment requires careful planning around space allocation, infrastructure requirements, and design integration. Understanding these considerations upfront prevents costly modifications and ensures optimal system performance throughout the facility's operational life.
Space Requirements
- U-space trade-off – Cooling units occupy rack positions
- Service clearance – Plan for maintenance access
- Aisle width – Ensure adequate space for airflow and service
Infrastructure Needs
| System Type | Infrastructure Requirements |
|---|---|
| Chilled Water | Existing or new chilled water loop, piping, controls |
| DX Systems | Electrical power, condensate drainage, refrigerant lines |
| Both Types | Control network, monitoring integration, service access |
Design Planning
- Cooling load analysis – Calculate heat generation per rack
- Airflow modeling – Verify adequate air circulation
- Redundancy planning – Ensure backup cooling capacity
- Future expansion – Design for growth and density increases
Best Practices for Deployment
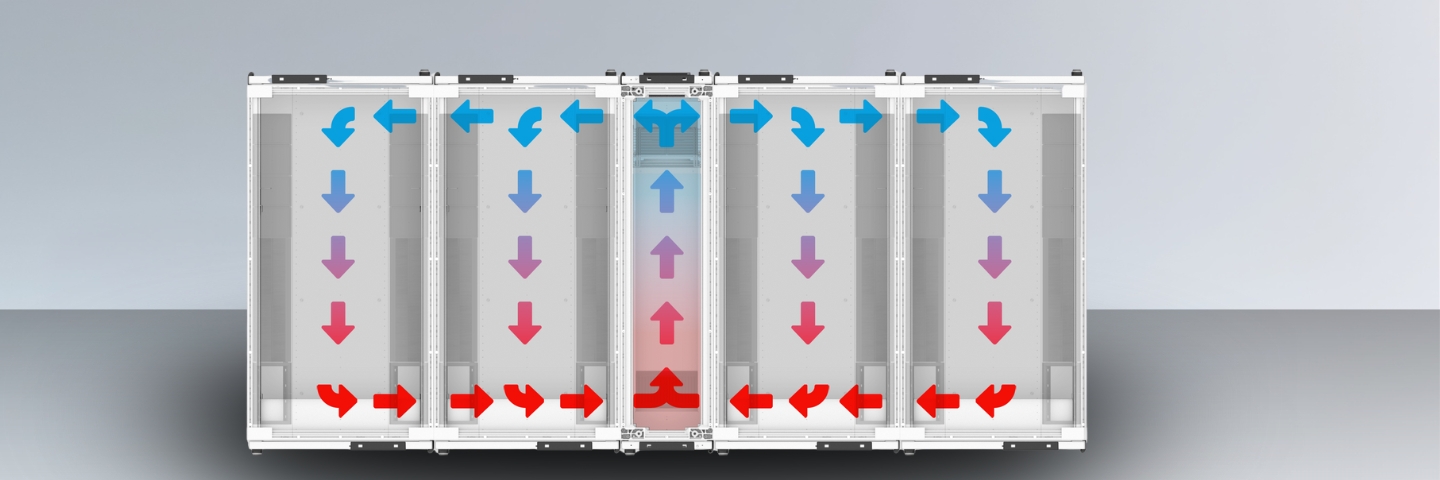
Effective row based cooling deployment follows established engineering principles and operational best practices. These guidelines help ensure optimal performance, energy efficiency, and long-term reliability while avoiding common implementation pitfalls that can compromise system effectiveness.
1. Proper Sizing
- Calculate total heat load per row
- Include safety margin (15–20% overcapacity)
- Consider future density increases
2. Strategic Placement
- Position units to optimize airflow patterns
- Maintain service access on all sides
- Coordinate with containment systems
3. Control Integration
- Connect to facility monitoring systems
- Set appropriate temperature setpoints
- Configure alarm thresholds and notifications
Performance Optimization
Maximizing row based cooling efficiency requires ongoing attention to system tuning, maintenance practices, and performance monitoring. These optimization strategies help reduce energy consumption while maintaining precise environmental control and extending equipment lifespan.
Energy Efficiency Tips
- Variable speed control – Adjust fan speeds based on load
- Temperature optimization – Raise supply temperatures when possible
- Regular maintenance – Keep coils and filters clean
- Monitoring integration – Track performance metrics continuously
Maintenance Requirements
- Monthly: Visual inspection, filter checks
- Quarterly: Coil cleaning, condensate drain verification
- Annually: Control calibration, refrigerant checks (DX systems)
When Row Based Cooling Makes Sense
Row based cooling excels in specific scenarios where traditional cooling methods fall short, but it's not universally the best solution. Understanding the ideal use cases and limitations helps determine when this technology provides the greatest value and return on investment.
Ideal Scenarios
- Low to medium rack densities (10+ kW per rack)
- Variable or unpredictable loads requiring responsive cooling
- Space-efficient designs where perimeter cooling isn't feasible
- Modular deployments needing scalable cooling solutions
- Containment strategies requiring close-coupled cooling
Consider Alternatives When
- Low rack densities (under 5 kW per rack)
- Uniform, predictable loads well-served by perimeter systems
- Extreme space constraints where U-space is critical
- Limited maintenance access in rack environments
Legrand Data Center Cooling Solutions
Implementing advanced cooling technologies requires the right infrastructure support and expertise. Legrand provides comprehensive solutions for modern data center thermal management, from power distribution and monitoring to physical infrastructure that enables optimal cooling performance.
Explore Legrand's cooling infrastructure solutions:
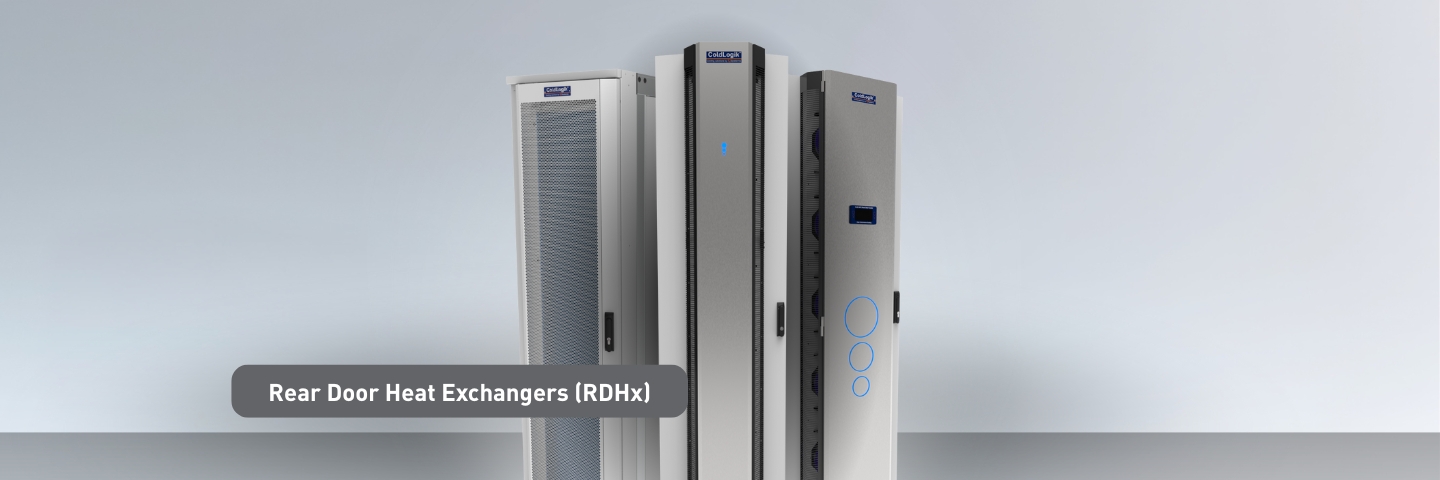

- Rear-Door Cooling Solutions – Complete infrastructure support for RDHx implementations, including power distribution, monitoring, and control systems designed for rack-level cooling technologies.

- Row-Based Cooling Infrastructure – Integrated solutions supporting in-row cooling deployments, featuring optimized power delivery, environmental monitoring, and cable management systems.
Our data center specialists can help you design and implement the infrastructure foundation that enables successful cooling technology deployment while ensuring reliability, efficiency, and scalability for your facility's evolving needs.
Conclusion
Row based cooling bridges traditional air cooling and advanced liquid cooling by delivering precise, efficient thermal management directly where heat is generated. This approach provides the control and efficiency needed for modern high-density computing while maintaining the simplicity and familiarity of air-based cooling systems.
For data centers facing increasing power densities, unpredictable workloads, or space constraints, row based cooling offers a proven path to improved thermal management and energy efficiency. The modular nature allows incremental deployment, making it an ideal solution for both new builds and retrofit applications.
As computing demands continue to grow, row based cooling remains a practical, scalable solution for maintaining optimal operating conditions while maximizing energy efficiency and operational control.



















 Canada
Canada
 Latin America (English)
Latin America (English)
 Latin America (Espanol)
Latin America (Espanol)
 USA
USA
 China
China
 India
India
 Japan
Japan
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 South East Asia (English)
South East Asia (English)
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 France
France
 Germany
Germany
 Italy
Italy
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Spain
Spain
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Turkey
Turkey
 UK
UK
 Africa (english)
Africa (english)
 Africa (français)
Africa (français)
 Middle East (english)
Middle East (english)
 Australia
Australia
 New Zealand
New Zealand





