Our Guide to Data Center Power Supply | What You Must Know
Guide to Data Center Power Supply
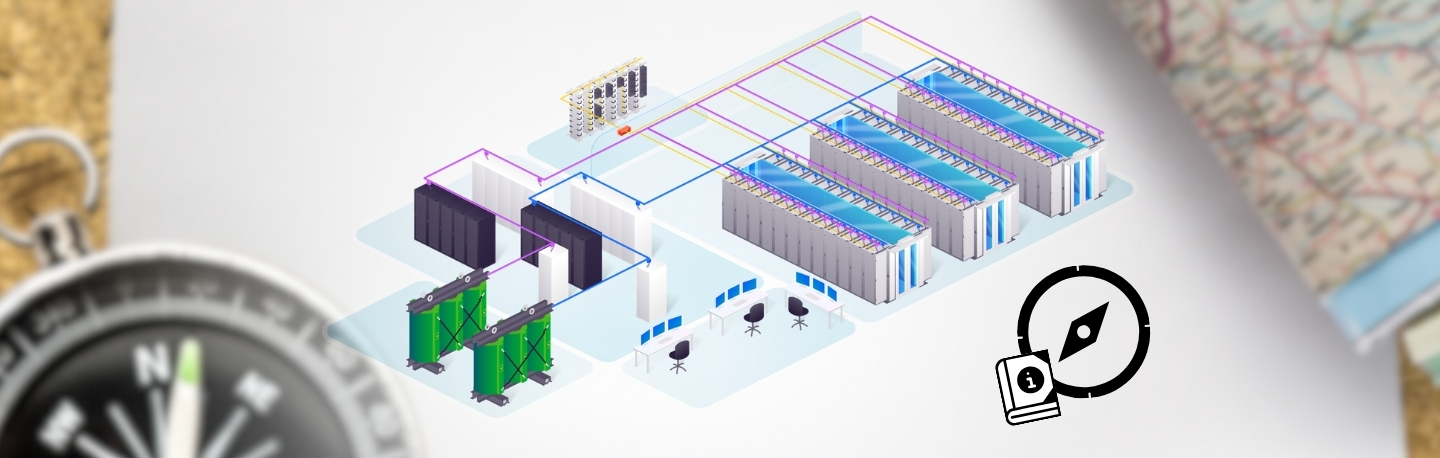
Power is everything in a data center. Without reliable electricity, your servers become expensive paperweights, your cooling systems fail, and your business stops.
Yet power infrastructure remains one of the most misunderstood aspects of data center design. This backwards approach costs the industry millions in downtime and inefficiency.
Why Data Center Power Demands Precision
Modern data centers consume enormous amounts of energy – hyperscale facilities require 20 to 100 megawatts or more. Today's IT equipment demands clean, stable power delivered at precise voltages. Server power supplies, whether bronze, platinum, or higher efficiency ratings, all depend on consistent electrical input.
The stakes are high. Downtime costs range from 137 pounds or euros per minute to over 1 million per hour for large enterprises. UPS failures remain the leading cause of these outages, making power infrastructure design critical for business continuity.
Essential Power Metrics Every Manager Should Track

Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE)
PUE measures total facility power consumption against IT equipment power consumption. Industry leaders target 1.2 or lower – meaning for every watt your servers use, only 0.2 additional watts go to cooling, lighting, and other support systems. Achieving this requires careful attention to power supply efficiency and infrastructure design.
UPS and Efficiency Ratings
UPS carry efficiency ratings from standard bronze (80% efficiency) through platinum levels (over 90% efficiency). Higher efficiency reduces heat generation, cutting cooling costs. When designing systems, waste heat directly impacts cooling requirements and operating expenses.
Capacity Planning Requirements
Effective capacity planning means understanding both current draw and future growth. Calculate total power requirements across different server form factors, from traditional 1U systems to high-density blade configurations. Smart designers build in 20-30% additional capacity to avoid costly upgrades.
How Power Flows Through Your Data Center
AC Power Distribution
Most facilities use alternating current (ac) systems, receiving power from the utility grid at medium voltage. This ac power follows a specific path:
Utility Connection → MV Main Switchgear → Transformers → LV Switchgear → UPS Systems → Power Distribution Units → PDUs → Server Racks
Power enters the data center through the utility connection and passes first through medium voltage switchgear for safe control. Transformers then step the voltage down to low voltage, which is distributed via the Low Voltage Main Switchboard. From there, distribution panels route power to UPS systems, which provide backup and clean electricity. Finally, Power Distribution Units (PDUs) deliver power to the server racks.
The Role of DC Power
Whilst ac dominates data center distribution, direct current (dc) plays crucial roles. UPS batteries store dc power for emergency backup. Modern server power supplies convert incoming ac to dc for processors and storage devices. Some facilities experiment with end-to-end dc distribution to eliminate conversion losses.
Modular Power Architectures
Modular power architectures offer significant advantages for growing facilities. Instead of installing oversized systems from day one, modular designs let you add capacity incrementally. This reduces initial costs while maintaining flexibility. A prime example of this approach is Legrand’s modular UPS systems, which scale seamlessly to match evolving power demands.
Critical Power Infrastructure Components
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS)
UPS systems form the backbone of data center power protection. These systems provide instant backup during utility outages whilst conditioning power to protect against voltage fluctuations and electrical noise. Modern UPS designs achieve 96% efficiency whilst delivering enterprise-grade reliability.
Three main UPS types serve different applications:
- Standby UPS: Basic protection for smaller loads
- Line-Interactive UPS: Mid-range protection with voltage regulation
- Online Double-Conversion UPS: Highest protection level for critical systems
Power Distribution Units (PDUs)
PDUs distribute electricity from UPS systems to individual server racks. Basic PDUs provide simple power distribution, whilst intelligent models offer monitoring, remote switching, and environmental sensing. Advanced PDUs help prevent circuit overloads and enable precise power management at the rack level.
Backup Generators
When utility power fails for extended periods, backup generators maintain operations. Modern generator systems integrate seamlessly with UPS equipment, automatically starting when needed and synchronising with existing power infrastructure. Proper generator sizing ensures adequate capacity for both IT loads and essential facility systems.
Cables and Connectivity
Power cables and connectors are critical for reliable operation. High-quality cables reduce resistance losses and heat generation. Proper cable management prevents accidental disconnections and simplifies maintenance. In high-density environments, cable selection directly impacts airflow and cooling.
High Power Busbars and Busway
As an alternative to traditional cabling, busway and high-power busbars offer flexible, efficient power distribution in grey space and white space. They simplify layout changes, improve cooling dynamics, and support higher power densities with reduced maintenance.
These systems provide tap-off points at regular intervals, allowing power connections to be added or relocated without major infrastructure changes. This flexibility makes them particularly valuable for growing data centers and facilities requiring frequent reconfigurations.
Common Power Supply Challenges
Scalability Constraints
Many data centers hit power walls as they grow. Initial designs become bottlenecks when computing density increases. The solution lies in flexible infrastructure that can expand without major renovations. Overhead busway systems allow power taps anywhere along the route without rewiring.
Efficiency Optimization
Poor power efficiency wastes money and generates excess heat. Common culprits include oversized UPS systems running at low loads, inefficient power supplies, and inadequate power factor correction. Regular audits help identify improvement opportunities and quantify potential savings.
Maintenance Windows
Traditional power infrastructure often requires scheduled outages for maintenance. Hot-swappable components eliminate many maintenance windows. Modular UPS’s allow component replacement without affecting running equipment, maximizing uptime.
Regulatory Compliance
Energy efficiency regulations continue tightening across Europe and globally. Data centers must balance performance requirements with environmental obligations. Modern power systems help meet these standards whilst reducing operational costs and carbon footprints.
Designing for Reliability and Growth
Redundancy Strategies
Single points of failure have no place in critical power infrastructure. N+1 redundancy provides backup for any single component failure. 2N redundancy offers complete duplicate systems. The right approach depends on your uptime requirements, budget constraints, and risk tolerance.
Monitoring and Management
You can't manage what you don't measure. Comprehensive power monitoring tracks everything from utility input to individual rack consumption. Modern systems provide real-time alerts, trend analysis, and predictive maintenance capabilities.
Future-Proofing Considerations
Technology evolution drives changing power requirements. Edge computing, artificial intelligence, and quantum systems all have unique electrical needs. Flexible infrastructure accommodates these changes without major disruption. Standard interfaces, modular components, and excess capacity provide adaptation pathways.
The Bottom Line
Data centers uninterruptible power supply isn't just about keeping equipment running – it's about enabling business success through reliable, efficient infrastructure. Whether you're planning a new facility or upgrading existing systems, the principles remain constant: design for reliability, plan for growth, and never compromise on quality.
The investment in proper power infrastructure pays dividends through reduced downtime, lower operating costs, and the confidence that comes from knowing your systems can handle whatever challenges arise. In a world where digital services never sleep, your uninterruptable power systems shouldn't either.
For comprehensive UPS solutions designed specifically for data center environments, explore our complete range of UPS and power management systems. Our experienced team can help design infrastructure that meets your current needs while providing flexibility for future growth.
Discover Also
- Key Electrical Equipment Used in Data centers
- Three-Phase UPS Systems Explained
- Online Double Conversion UPS Technology: Power Protection Guide
- Different Types of UPS: Complete Guide to Uninterruptible Power Systems
- Predictive Maintenance: Revolutionizing UPS Reliability and Battery Optimization
- Three-Phase UPS: Power, Voltage, and System Architecture Guide
- MTTR and MTBF: Key Metrics for Maximizing UPS Reliability and Uptime
- Understanding UPS Capacity: A Practical Guide for Technical Decision-Makers
- Sustainable Data Centers: Delivering Lower Emissions Through High-Performance Keor FLEX UPS
- Data Center Optimization: Enhancing Performance, Efficiency & Resilience
- Data Center Electrical Safety: Designing Compliant and Resilient Power Infrastructure
- Transformerless UPS Systems: Efficiency, Flexibility, and Performance for Modern Applications
- A Technical Guide to UPS Selection: Matching Systems to Real-World Requirements



















 Canada
Canada
 Latin America (English)
Latin America (English)
 Latin America (Espanol)
Latin America (Espanol)
 USA
USA
 China
China
 India
India
 Japan
Japan
 Republic of Korea
Republic of Korea
 South East Asia (English)
South East Asia (English)
 Austria
Austria
 Belgium
Belgium
 France
France
 Germany
Germany
 Italy
Italy
 Netherlands
Netherlands
 Spain
Spain
 Switzerland
Switzerland
 Turkey
Turkey
 UK
UK
 Africa (english)
Africa (english)
 Africa (français)
Africa (français)
 Middle East (english)
Middle East (english)
 Australia
Australia
 New Zealand
New Zealand